In a first step, the gradient images are derived from the original images and "landmark" features are detected via threshold criteria (Figure 1).
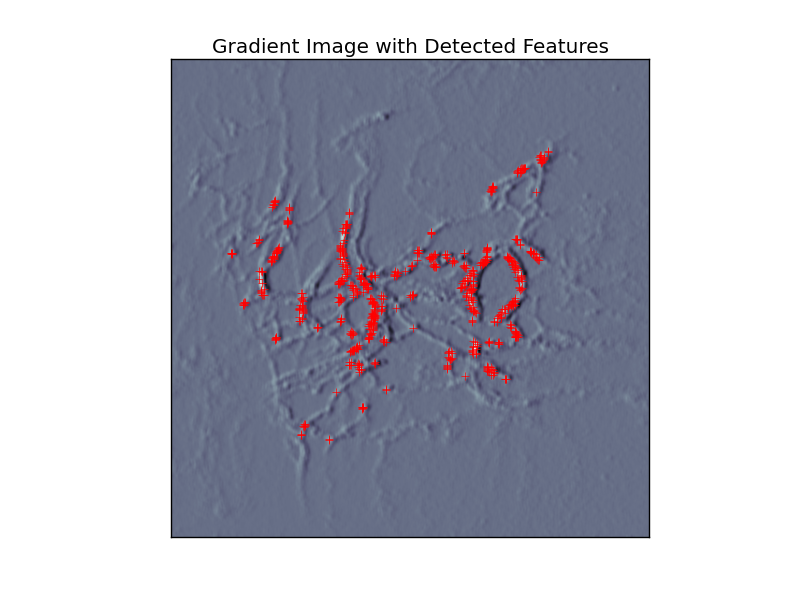 |
| Figure 1 |
In a second step, affine transformation is applied to the matching image via optimization method until a defined distance criteria (nearest neighbor criteria with KDTree) between the landmarks reached a minimum (Figure 2).
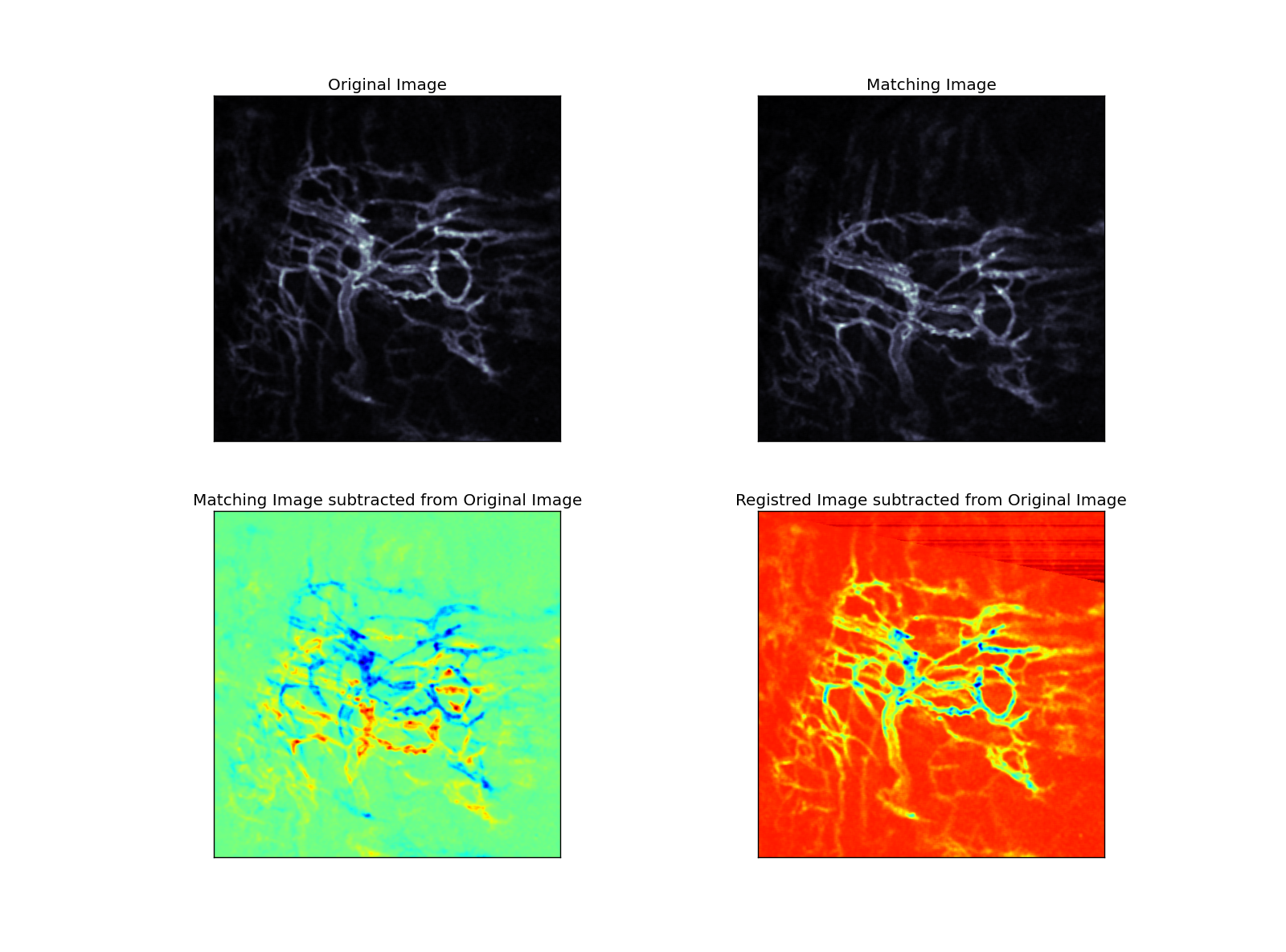 |
| Figure 2 |
The Python code:
'''
@author: Christian Rossmann, PhD
@license: Public Domain
@blog: http://scientificcomputingco.blogspot.com/
'''
from scipy import ndimage
from scipy.spatial import cKDTree
from scipy.optimize import fmin
def register(im1,im2):
# initialize the transformation matrix
T = [[1.0,0.0],[0.0,1.0]]
# extract features from first image
edges1 = ndimage.sobel(im1)
features1 = dstack(where(edges1.T > edges1.mean()))[0]
kd = cKDTree(features1)
def errfunction(T,kd=kd,im2=im2):
# transform the image
img = ndimage.interpolation.affine_transform(im2,T.reshape(2,2))
# extract features from transformed image
edges = ndimage.sobel(img)
features = dstack(where(edges.T > edges.mean()))[0]
dst,idx = kd.query([features])
# measure the distances between features.
return sum(dst**2)
T = fmin(errfunction,T,xtol=1.e-6,ftol=1.e-6,maxfun=5000,maxiter=5000)
return (T,ndimage.interpolation.affine_transform(im2,T.reshape(2,2)))
im1 = imread("sample_images/IMG1.png")[:,:,0]
im2 = imread("sample_images/IMG2.png")[:,:,0]
im1 = ndimage.filters.uniform_filter(im1,5)
im2 = ndimage.filters.uniform_filter(im2,5)
im1 -= im1.min(); im1 /= im1.max()
im2 -= im2.min(); im2 /= im2.max()
(T,rimg) = register(im1,im2)
#%%
figure(1)
clf()
s = subplot(1,1,1)
title('Gradient Image with Detected Features')
imshow(edges,'bone')
edges = ndimage.sobel(im1)
features = dstack(where( (edges.T > 0.45) & (edges.T < 0.55) ))[0]
plot(features[:,0],features[:,1],'+',color='red')
xlim([0,im1.shape[0]])
ylim([0,im1.shape[1]])
s.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
s.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
#%%
figure(2)
clf()
s = subplot(2,2,1)
title('Original Image')
imshow(im1,'bone')
s.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
s.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
s = subplot(2,2,2)
title('Matching Image')
imshow(im2,'bone')
s.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
s.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
s = subplot(2,2,3)
title('Matching Image subtracted from Original Image')
imshow(im2-im1,'jet')
s.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
s.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
s = subplot(2,2,4)
title('Registred Image subtracted from Original Image')
imshow(rimg-im1,'jet')
s.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
s.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
show()
